eBPF Overview
Cilium is an open-source solution providing security, observability and networking for cloud-native workloads. Cilium uses Kernel eBPF, it basically allows to run sandbox on operating systems which can be used by developers to create and run eBFP-based programs to cover a various gaps about observability and tracing, network isolation and security as never seen before without any changes required to the Kernel or extra kernel modules that could affect security or stabilization.
Traditionally, the linux kernel is designed to be stable and the core of the operating system, its standards for security and stability are high and most of the external functionality are loaded via modules to be loaded on demand or at bootime.
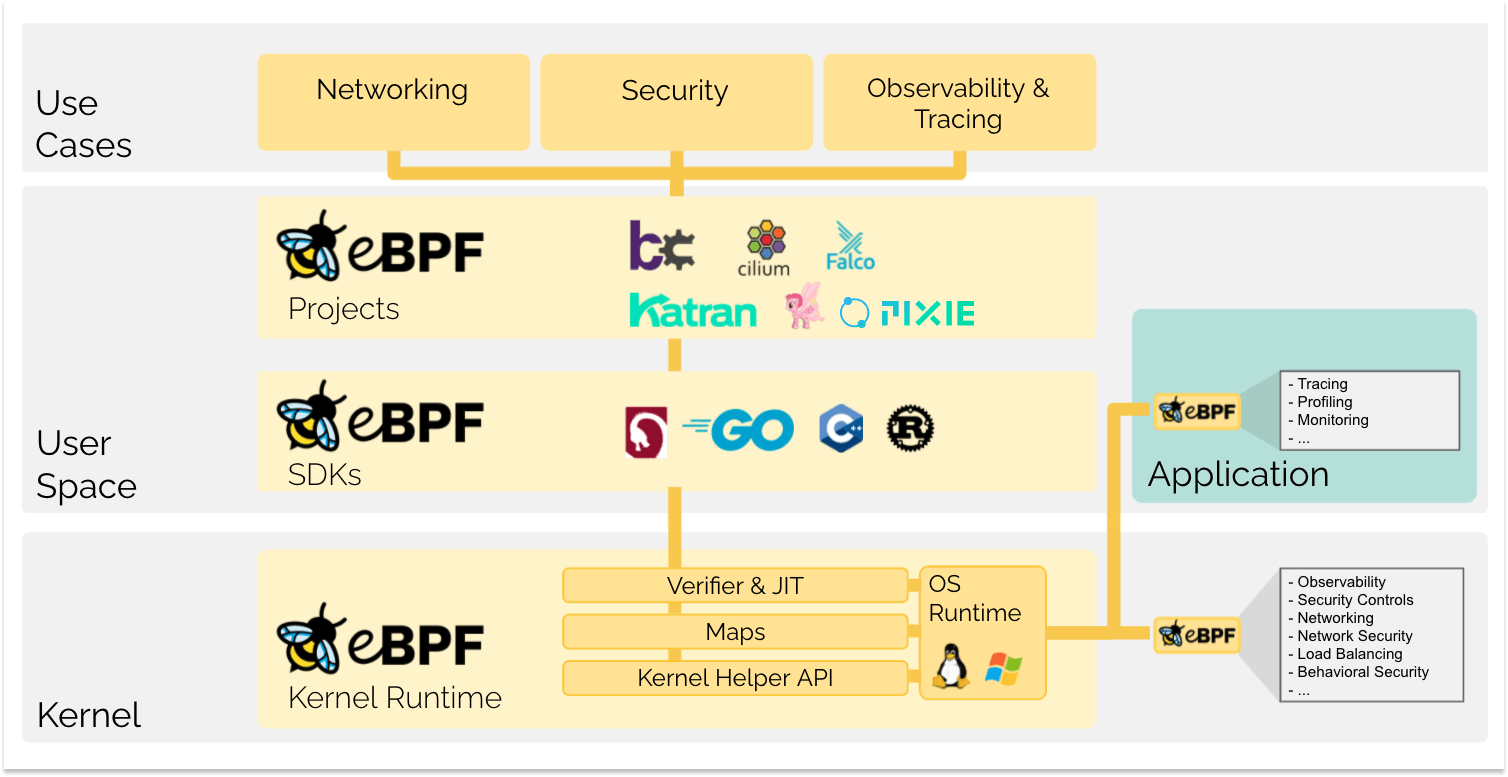
Along with the initiatives of the projects around eBPF, there are several enterprise-level projects powered by eBPF technology such as Katran, Pixie, Falco or Cilium
Introduction to Cilium
Cilium a cloud-native layer 7 networking and security solution powered by eBPF. Thanks to eBPF, provides granularity and observability which can be accessed through the LSM (Linux Security Module) and eBFP.
Some of Cilium features:
- Secure Networking: Cilium leverages Linux Security Module (LSM) and eBPF to provide granular control over network access and visibility.
- High-Performance Networking: Cilium enables low-latency and high-throughput networking with a combination of eBPF-based packet filtering and XDP-based acceleration.
- Scalability: Cilium provides a scalable networking solution that can handle thousands of nodes and millions of workloads.
- Easy of usage: Cilium is provided through a cli which makes it easier to deploy, manage and control all the required components.
Deploy local cluster with Kind
Cilium on Kubernetes is provided as a CNI, so installation will fail unless disable the default CNI, make sure to disable it on the kind configuration file.
kind: Cluster apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4 nodes: - role: control-plane - role: worker - role: worker - role: worker networking: disableDefaultCNI: true
Use the config above to deploy a local cluster
kind create cluster --config ~/kind-configs/kindconfig.yaml Creating cluster "kind" ... ✓ Ensuring node image (kindest/node:v1.26.3) 🖼 ✓ Preparing nodes 📦 📦 📦 📦 ✓ Writing configuration 📜 ✓ Starting control-plane 🕹️ ✓ Installing StorageClass 💾 ✓ Joining worker nodes 🚜
None of the workers will go Ready until Cilium is enabled
❯ kc get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
kind-control-plane NotReady control-plane 6m18s v1.26.3
[...]
message: 'container runtime network not ready: NetworkReady=false reason:NetworkPluginNotReady
message:Network plugin returns error: cni plugin not initialized'
Deploy Cilium CNI with CLI
Use the cli (how to install Cilium CLI) to deploy Cilium.
❯ cilium install 🔮 Auto-detected Kubernetes kind: kind ✨ Running "kind" validation checks ✅ Detected kind version "0.18.0" ℹ️ Using Cilium version 1.13.0 [...] Cilium was successfully installed! Run 'cilium status' to view installation health
Cilium is ready to be used, nodes should go into Ready status along with the successful of required components.
As it is serving as a CNI, by default, it runs on kube-system as a privilege container
securityContext:
privileged: true
Introduction to Hubble
Hubble is a powerful tool that provides visibility into network traffic in a Kubernetes cluster. It can help you identify issues and improve your understanding of how your applications communicate with each other. Hubble leverage Cilium to provide advanced networking observability.
To get started with Hubble, first of all it needs to be deployed as a cilium component using the above CLI.
❯ cilium status --wait
/¯¯\
/¯¯\__/¯¯\ Cilium: OK
\__/¯¯\__/ Operator: OK
/¯¯\__/¯¯\ Hubble Relay: OK
\__/¯¯\__/ ClusterMesh: disabled
\__/Once enabled, Hubble uses eBPF technology to monitor traffic and detect any anomalies or bottlenecks
With Hubble, traffic can be observed in real time which leverage the ability to react proactively even before affects any production applications.
The Hubble UI Architecture
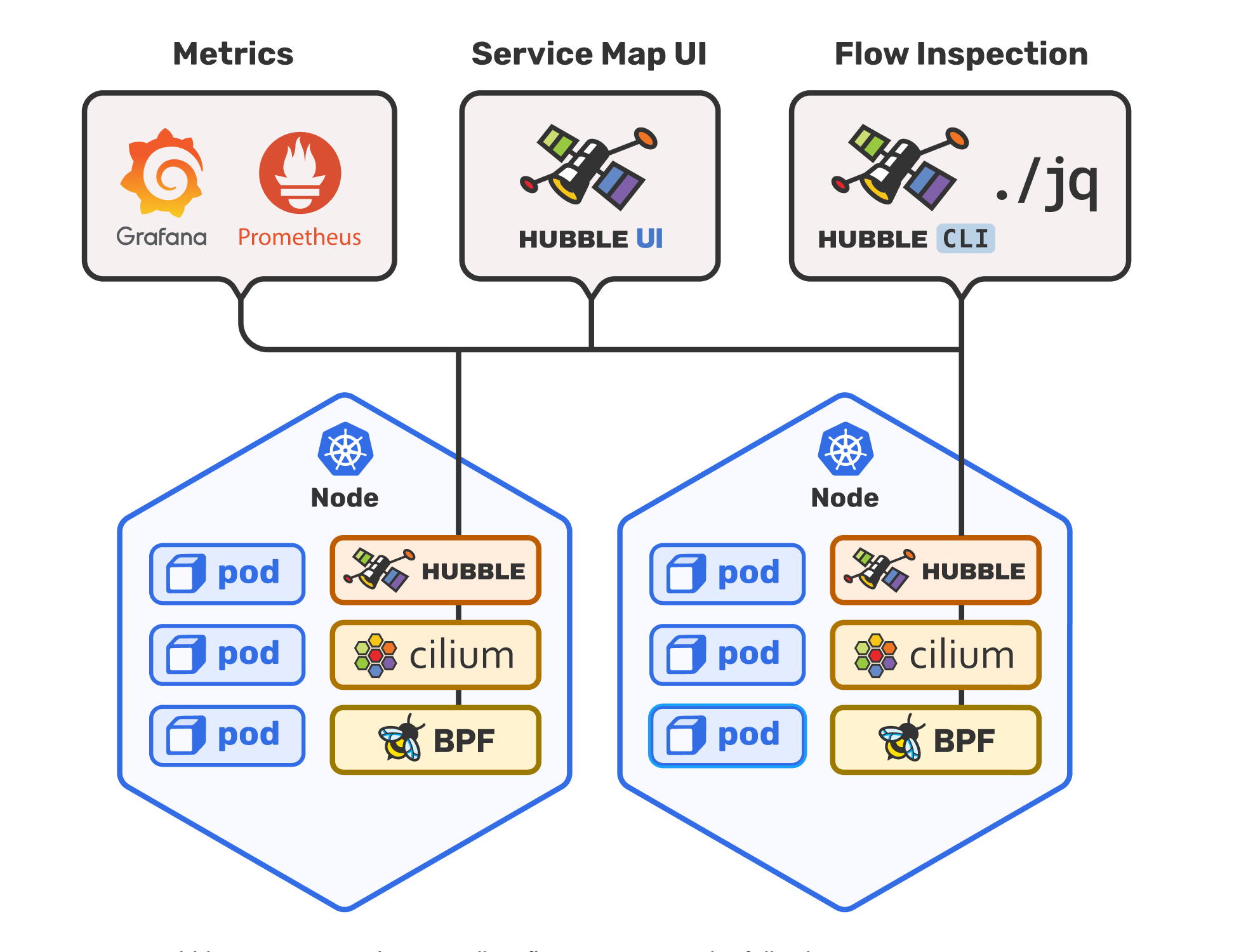
The Hubble architecture consistes on a set of deployments managed by a Cilium Operator which is installed via the cilium install performed during the initial Cilium deployment. These components will be spreaded across the nodes to ensure the advanced networking capabilities
Along with the components deployed, required deployments will be managed by the operator itself, for Cilium and Hubble these are the following:
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE cilium-operator 1/1 1 1 37h hubble-relay 1/1 1 1 11h hubble-ui 1/1 1 1 11h
Enable Hubble component with UI
Hubble can work using the command line only or the UI, enable it using the Cilium cli.
❯ cilium hubble enable --ui 🔑 Found CA in secret cilium-ca [...] ✨ Deploying Hubble UI and Hubble UI Backend... ⌛ Waiting for Hubble to be installed... ℹ️ Storing helm values file in kube-system/cilium-cli-helm-values Secret ✅ Hubble was successfully enabled!
Before accessing the UI, redirect the ports as follows:
❯ kubectl port-forward -n kube-system svc/hubble-ui --address 0.0.0.0 --address :: 12000:80 Forwarding from 0.0.0.0:12000 -> 8081 Forwarding from [::]:12000 -> 8081
The UI is accessible at http://localhost:12000
Observe traffic with Hubble
The easiest way to test real time monitoring is executing the connectivity test and follow the process with the Hubble UI. Filter by the namespace == cilium-test to see the architecture and how the traffic works along the different services.

Through the advanced networking feature powered by eBPF, the traffic generated by the cilium connectivity test, can be monitored so any unexpected external communication to world, host is detected immediately.
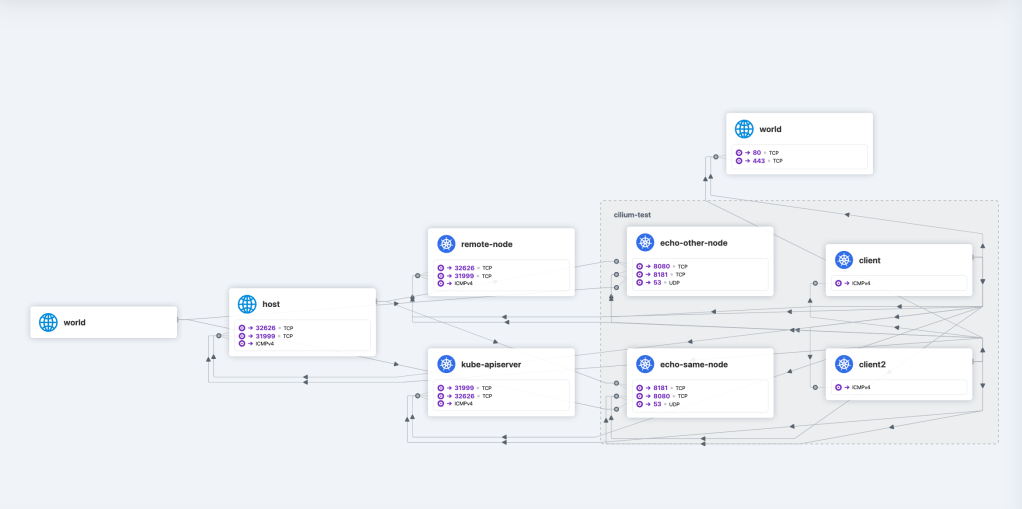
With the above dashboard you can immediately detect outbound/inbound traffic and start analyzing it at a deeper level, not only limiting traffic from or to any endpoint.
Target services and ports are attached to each identified objects in the dashboard allowing even to identify traffic that coming out the namespace or even when multiple namespaces are involved in the communication.
By the usage of Cilium Policies, any of the above communication can be blocked in an “allow-all-BUT” policy type or just denying everything not recognized as part of the application architecture expected traffic.
Any of the above can be inspected just selecting from the column below the graph.
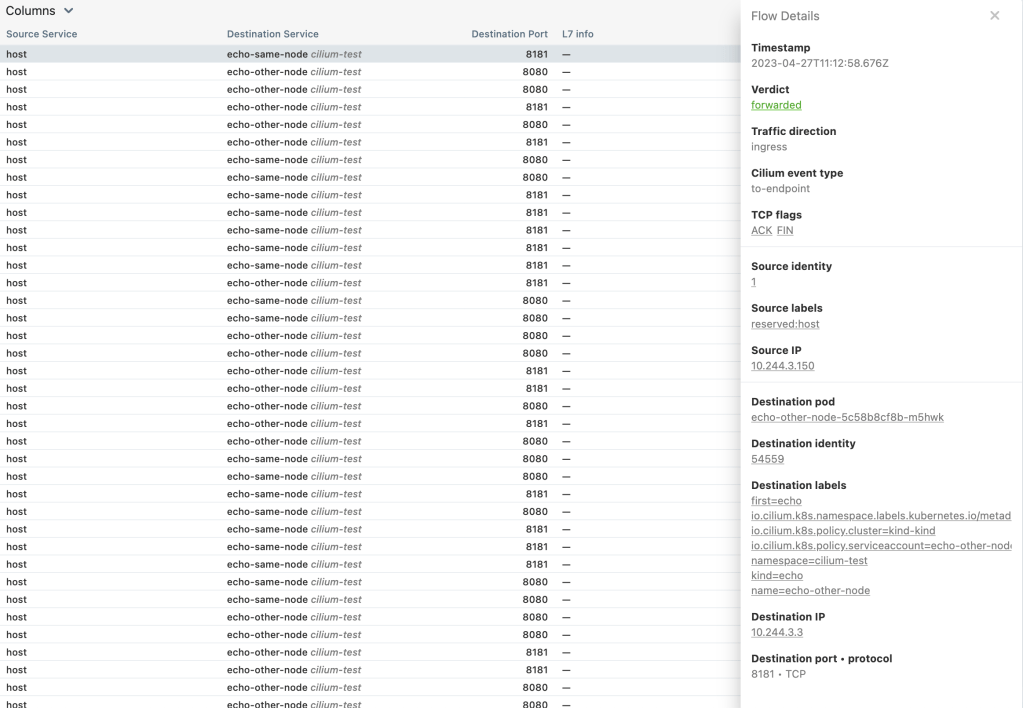
The insights about the selected traffic show specific information like:
- Timestamp (when the communication was issued)
- Traffic direction
- TCP Flags
- Source and Destination IPs
- Destination object, ports and Protocols
- Source labels
The combination of the above allows different teams to improve the environment when it comes to get better network performance, identification and fix bottlenecks while keeping the highest security standards for production environments.
Advantadges of network observability with Hubble and Cilium Policies
Cilium and Hubble provide a powerful new approach to network observability. With eBPF, you can monitor and analyze traffic at deeper level, allowing to detect and understand unexpected behavior.
Hubble not only analyze the traffic but also leverage the policy engine that comes with Cilium to automatically block any unrecognized traffic or perform specific actions based on the policy definition.
Cilium is designed for Kubernetes, is a cloud-native solution making it flexible and easy to integrate with other commponents like Istio or Grafana for instance. Cilium don’t require to be used as a full stack, it can be easily integrated with an existing environment where all the components or only a part of them can be used depending on your needs.
Conclusion
If you are looking for a cloud-native network observability solution, Cilium and Hubble should be considered a way-to-go as it leverages eBPF to provide granularity and real-time traffic observability.
With the policy driven approach coming with Cilium and Hubble network analysis feature, you can ensure workloads are running safely and efficiently.
With all the information provided by the UI through the usage of eBPF, you can improve application performance, understand network usability and being proactive to take better decisions in terms of network security and optimization. The robust capabilities of Cilium and Hubble enable teams to gain network visibility and manage it more efficiently on a Kubernetes infrastructure.
